Sustainability 2025, 17(13) – Published: 3 July 2025
This article belongs to the Special Issue Sustainable Organization Management
and Entrepreneurial Leadership
and Entrepreneurial Leadership
Abstract
This study investigates the relationships between entrepreneurial leadership skills (ELSs), ethical entrepreneurial leadership (EEL), corporate sustainable development (CSD), and competitive advantage (CA) in SMEs. Drawing on resource-based view theory, we examine whether entrepreneurial capabilities and ethical practices jointly contribute to sustainability and competitive positioning. Data from 312 SME leaders across manufacturing, services, technology, and trading sectors were analyzed using PLS-SEM. Results reveal that ELSs foster EEL (β = 0.684, p < 0.001) and enhance CSD (β = 0.453, p < 0.001). EEL significantly affects CSD (β = 0.527, p < 0.001) and partially mediates the relationship between entrepreneurial skills and sustainability (indirect effect = 0.361). CSD strongly enhances CA (β = 0.612, p < 0.001). 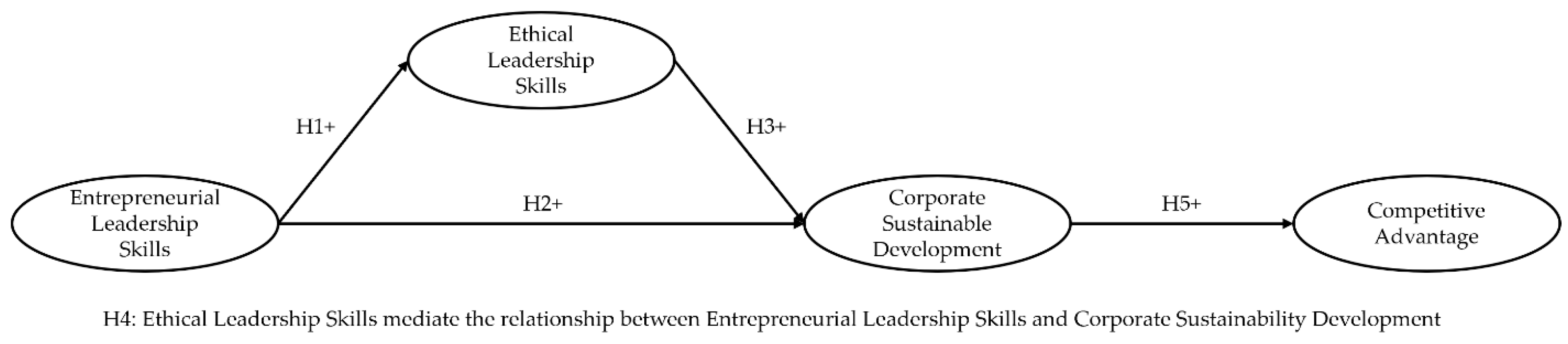
The findings demonstrate that integrating entrepreneurial capabilities with ethical leadership creates foundations for sustainable development and CA in resource-constrained environments.
This research extends entrepreneurial leadership theory by showing complementarity between entrepreneurial and ethical orientations, advances sustainability theory by revealing ethical leadership’s mediating role, and enriches RBV by demonstrating how intangible leadership capabilities generate CA when traditional resources are scarce. Practical implications include developing integrated leadership programs and sustainability frameworks for emerging economy SMEs.

The findings demonstrate that integrating entrepreneurial capabilities with ethical leadership creates foundations for sustainable development and CA in resource-constrained environments.
This research extends entrepreneurial leadership theory by showing complementarity between entrepreneurial and ethical orientations, advances sustainability theory by revealing ethical leadership’s mediating role, and enriches RBV by demonstrating how intangible leadership capabilities generate CA when traditional resources are scarce. Practical implications include developing integrated leadership programs and sustainability frameworks for emerging economy SMEs.
Keywords: entrepreneurial leadership; ethical leadership; corporate sustainable development; competitive advantage; resource-based view; SMEs; business ethics; organizational sustainability; innovation; strategic management



